Welcome to the ultimate guide on how to avoid making mistakes that can lower your cold email success rate. As a seasoned expert in cold email marketing, I have witnessed firsthand the incredible impact that well-crafted cold emails can have on business communication. These emails are not just another mundane task; they hold immense potential for driving growth and opening doors to valuable opportunities.
Click here to read our informative guide to cold email success rates!
When executed with finesse, cold email campaigns become an indispensable tool for expanding your network, generating high-quality leads, and ultimately boosting sales. By carefully crafting personalized messages tailored to individuals who perfectly align with your ideal customer profile, you will effortlessly capture their attention and ignite their curiosity about what you bring to the table.
However, it is crucial to be aware of common pitfalls that can sabotage your efforts and diminish your cold email success rates. In the upcoming section, we will delve into these missteps in detail so that you can steer clear of them and unleash the full potential of your cold email campaigns.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Creating Cold Emails
When it comes to cold email marketing, knowing how to write effective emails and get higher response rates is crucial. However, there are common mistakes that many people make when sending out their cold emails, which can significantly lower their success rate. Here, we will discuss these mistakes and provide you with valuable tips on how to avoid them.
- One of the most common mistakes in cold email outreach is not paying enough attention to the subject lines. The subject line is the first thing your recipients see, and it plays a vital role in whether or not they open your email. To increase your open rates, it’s important to craft compelling subject lines that grab attention and entice readers to click.
- Another mistake is sending generic emails without personalization. Personalizing your emails shows that you have taken the time to research and understand your recipients’ needs or pain points. By addressing them by name and mentioning specific details relevant to their business or industry, you can establish a connection right from the start.
- Failing to provide value in your initial email is another common oversight that can hinder your success rate. Instead of focusing solely on what you want from the recipient (such as a sale or partnership), highlight what benefits they will gain from engaging with you. Show them how your product or service can solve their problems or improve their business.
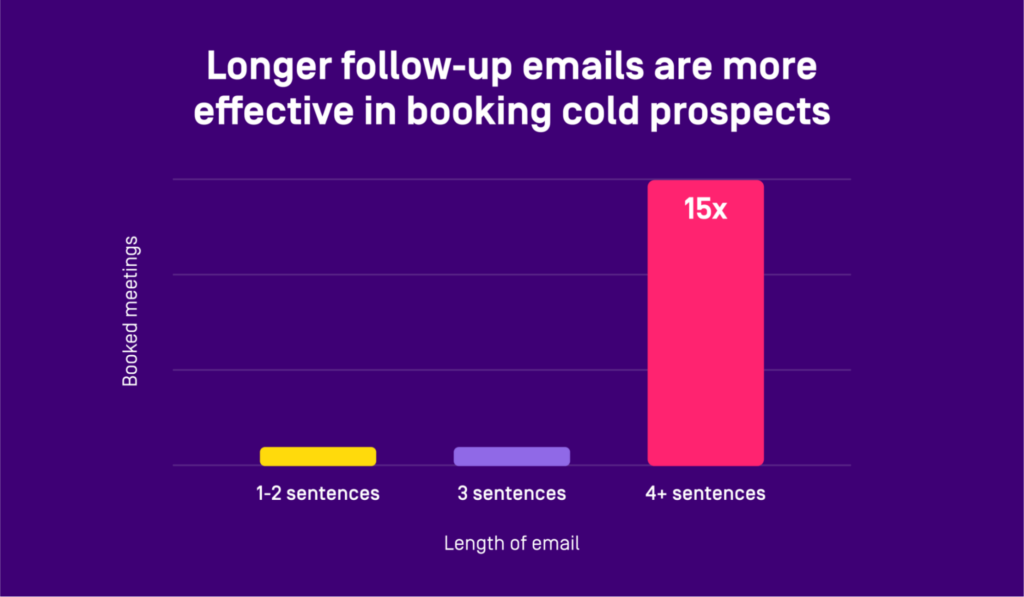
- Overlooking follow-up emails is a mistake that many people make when conducting cold outreach campaigns. Follow-ups are essential for nurturing relationships with potential clients who may have missed or overlooked your initial email. Sending polite reminders at appropriate intervals demonstrates persistence while maintaining professionalism.
- Neglecting proper proofreading before hitting send can be detrimental to the effectiveness of your cold emails. Grammatical errors and typos reflect poorly on both you and your company’s credibility. Take the time to review each email carefully, ensuring that it is error-free and conveys your message clearly.
- Not tracking and analyzing the results of your cold email campaigns can also hinder your progress. By monitoring open rates, response rates, and conversion rates, you can identify what strategies are working well and which ones need improvement. This data-driven approach allows you to make informed decisions for future outreach efforts.
In conclusion, understanding the common mistakes to avoid when sending cold emails is crucial for achieving higher success rates in your marketing endeavors. By paying attention to subject lines, personalizing your emails, providing value upfront, following up diligently, proofreading meticulously, and tracking campaign results consistently, you will be well on your way to optimizing the effectiveness of your cold email outreach.
Expert Tips on Maximizing Your Cold Email Success Rate
When it comes to cold email marketing, there are key mistakes that can have a detrimental impact on your success rate. We want to share with you some invaluable insights on how to avoid these pitfalls and achieve outstanding results in your outreach campaigns.
- Craft irresistible subject lines: Your subject line is the key to capturing your recipient’s attention and getting them to open your email. Neglecting this element is a huge mistake. Create compelling, personalized subject lines that stand out from the crowd and avoid being overlooked or sent to spam folders.
- Personalize for connection: Don’t let your emails get lost in the sea of generic messages. Personalize them to make a genuine connection with your audience. Take the time to understand their needs and interests, and tailor each email accordingly. This thoughtful approach will boost engagement levels significantly.
- Target your ideal audience: Find people who genuinely align with what you offer and are most likely interested in hearing from you! Prioritize quality over quantity to save resources and boost your reputation as a sender.
- Send follow-up emails: By reaching out to recipients who haven’t responded initially, you have a chance to gently remind them or address any concerns they may have had about your offer.
By implementing these expert tips into your cold emailing strategies, rest assured that you’re setting yourself up for higher success rates and more fruitful interactions with potential customers. Read the following sections to learn more about each point.
The Art of Crafting Effective Subject Lines
The power of your subject line in cold emailing is immense. It can determine whether your email gets opened with anticipation or ignored. Crafting effective subject lines is a skill that greatly impacts your success rate. Here are expert tips and tricks to engage your recipients:
- Make your subject line short, snappy, and straight to the point. Avoid vague phrases; instead, highlight specific benefits or offer irresistible solutions.
- Create an instant connection by using the recipient’s name, company name, or relevant information you’ve gathered during research.
- Incorporate words like “limited time offer” or “last chance” to create a sense of urgency that compels recipients to open immediately.
- Pose intriguing questions that ignite curiosity and leave recipients eager to uncover more by opening your email.
- Include numerical figures in your subject lines for added credibility among the flood of emails in everyone’s inbox.
Remember, crafting effective subject lines requires ongoing experimentation and adaptation.
The Power of Personalization
In the world of cold emailing, personalization is a game-changer. No more generic mass emails that end up in spam folders or get deleted without a second thought. In today’s competitive business landscape, personalization sets you apart and establishes genuine connections.
Why is personalization vital? Put yourself in their shoes. They receive countless emails daily, most of which they ignore or delete immediately. To avoid being brushed aside and increase your chances of getting a response, make your email feel crafted specifically for them.
Here are proven strategies for personalizing your cold emails:
- Explore their company background, understand their role, and stay updated on recent news related to them or their industry. Tailor your message and show that you genuinely care about connecting with them.
- Use their name instead of generic greetings like “Dear Sir/Madam.” Find out their name through LinkedIn profiles or other sources.
- If you have mutual connections with the recipient, mention them in your introduction to create familiarity and trust.
- Mention specific achievements or projects they’ve worked on that align with what you’re offering to demonstrate interest in what they do.
- Customize your value proposition to address the recipient’s pain points or challenges directly. Show how your product/service can solve their problems and capture attention.
Remember, personalization goes beyond inserting details into a template email—it’s about crafting a resonating message for the individual on the other side of the screen. Take time to understand recipients and tailor emails accordingly!
Choosing the Right Audience
When it comes to cold emailing, nothing is more important than reaching the right audience. Sending your emails to the wrong people can be a waste of time and effort, resulting in lower response rates. To ensure that your cold email campaigns hit the mark, here are some expert tips on how to identify and connect with the ideal audience:
1. Define Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)
Before you dive into sending out cold emails, take a moment to clearly define your ideal customer profile. This means understanding their industry, company size, job title, and pain points that align with what you offer. By knowing exactly who you’re targeting, you can craft personalized messages that have a higher chance of getting positive responses.
2. Conduct Thorough Research
Once you’ve identified your ICP, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research on potential prospects within that target group. Utilize powerful tools like LinkedIn or professional networking platforms to gather valuable information about their roles, responsibilities, and interests. Armed with this knowledge, you’ll be able to tailor your emails specifically for each recipient.
3. Segment Your Email List
Instead of blasting generic emails to everyone on your list, segment them based on specific criteria such as industry or job function. This allows you to create highly targeted messages that resonate with each segment’s unique needs and challenges.
4. Leverage Existing Relationships
If possible, leverage any existing relationships or connections when reaching out via cold email. Mention mutual contacts or shared experiences early on in order to establish credibility and trust from the get-go.
5. Test Different Audiences
Don’t shy away from experimenting with different audiences during your cold email campaigns! You might discover certain segments respond better than others or uncover new opportunities by exploring different niches within your target market.
Remember that choosing the perfect audience isn’t a one-time task; it requires continuous refinement and optimization based on data-driven insights from previous campaigns.
By investing time into identifying and connecting with the right audience, you significantly increase your chances of cold email success. Targeted emails are more likely to resonate with recipients, resulting in higher open and response rates. So take the time to research, segment your email list, personalize your messaging, and leverage existing relationships for maximum impact.
Avoiding Spam Filters
When it comes to cold emailing, ensuring that your emails reach the right people can be a daunting task. With spam filters becoming more sophisticated by the day, understanding their inner workings and how to avoid being labeled as spam is crucial.
Unlocking the Secrets of Spam Filters
Spam filters employ complex algorithms and criteria to determine whether an email is legitimate or junk. They scrutinize factors like subject lines, content quality, sender reputation, and recipient engagement. By grasping these key elements, you can take proactive measures to ensure that your emails steer clear of the dreaded spam folder.
Crafting Emails That Bypass Spam Filters with Ease
To dodge those pesky spam filters successfully, adhere to these best practices:
- Choose a reputable email service provider
Opt for a trusted email service provider renowned for its high deliverability rates. This will significantly increase the likelihood of your emails landing in recipients’ inboxes instead of getting lost in cyberspace.
- Personalize each email
Generic mass emails are prime targets for spam flags. Take the time to personalize every message by addressing recipients by name and tailoring content according to their specific needs or interests.
- Steer clear of excessive promotional language
Overusing promotional jargon or bombarding readers with exclamation marks often triggers spam filters’ alarm bells. Maintain a professional tone throughout your communication and focus on delivering value rather than pushing sales pitches.
- Optimize subject lines strategically
Subject lines wield immense power when it comes to enticing recipients into opening an email. Avoid using all caps or misleading phrases that might set off spam filters’ radar.
- Test before hitting send
Before unleashing a wave of cold emails upon unsuspecting prospects, conduct thorough testing by sending them first to yourself or colleagues who use different email providers. This way, you can identify and rectify any potential issues before they reach your target audience.
Safeguard Your Sender Reputation
Your sender’s reputation holds the key to determining whether your emails land in the inbox or vanish into spam oblivion. Keep a vigilant eye on your email deliverability rates and take proactive steps to maintain a stellar sender reputation. This includes regularly purging your email list, removing inactive subscribers, and promptly addressing any spam complaints that may arise.
Offer Clear Opt-Out Options
Including transparent opt-out options in your emails not only ensures compliance with anti-spam regulations but also enhances your sender’s reputation. Make it effortless for recipients to unsubscribe from future emails if they no longer wish to receive them.
By following these expert tips, you can significantly increase the likelihood of your cold emails reaching their intended recipients’ inboxes instead of being flagged as spam. Remember, building trust and delivering value should be at the forefront of every cold email campaign if you want to achieve higher response rates while avoiding common mistakes that can hinder your success rate.
Measuring and Improving Cold Email Success Rate
Welcome to the ultimate guide on how to avoid common mistakes that can lower your cold email success rate. As a seasoned expert in the field, I understand the importance of achieving higher response rates and optimizing your approach. In this section, I will share my first-hand expertise and provide you with valuable tips on measuring and improving your cold email success.
Set Clear Goals
Before diving into measuring your cold email success rate, it is crucial to establish clear goals for your campaign. Whether you’re aiming for a specific number of responses or looking to increase conversions and sales, having well-defined objectives will serve as a compass throughout the process.
Track Open Rates
Monitoring open rates is essential when it comes to evaluating the effectiveness of your subject lines and ensuring that recipients are engaged with your emails. A low open rate may indicate that adjustments need to be made in order to captivate readers’ attention.
Monitor Response Rates
The response rate measures how many recipients actively engage with your cold emails by replying or taking desired actions. This metric reflects both the impact of your subject lines and the quality of your email content.
Analyze Conversion Rates
If driving conversions or sales through cold emailing is one of your primary goals, tracking conversion rates becomes paramount. This metric reveals how many recipients took action after opening and responding positively to an email.
Utilize Tracking Tools
To accurately measure these metrics, consider leveraging powerful tracking tools such as Google Analytics or specialized email marketing software designed specifically for cold emailing campaigns. These tools provide detailed analytics reports that offer invaluable insights into campaign performance.
A/B Testing
Experimentation plays a pivotal role in continuously improving cold email success rates over time. By conducting A/B tests using different versions of subject lines, body copy, call-to-action buttons, etc., you can identify which variations resonate best with your audience before implementing them on a larger scale.
Track Unsubscribes and Bounces
Monitoring unsubscribes and bounces is crucial for understanding how well your emails are resonating with your audience. A high unsubscribe rate may indicate the need to refine your messaging, while a high bounce rate could signal the necessity of cleaning up your email list or improving contact quality.
Seek Feedback
Don’t hesitate to ask for feedback from recipients who engage with your cold emails. Their insights can provide valuable information about what works well and areas that can be improved in future campaigns. So, use their feedback to pinpoint the areas for improvement and then come up with another strategy that will target those areas only.
Continuously Improve
Based on the data collected, make necessary adjustments to optimize your cold email strategy. Refine subject lines, personalize content further, fine-tune targeting criteria, or adjust sending timing based on recipient behavior patterns.
By consistently measuring and analyzing key metrics, you will uncover areas for improvement and take actionable steps toward increasing the success rate of your cold email campaigns.
Remember that successful cold emailing requires ongoing refinement and adaptation as you gain more knowledge about what resonates best with your target audience. Stay committed to tracking results and making data-driven decisions to achieve optimal outcomes.